2-Minute Neuroscience: The Hippocampus скачать в хорошем качестве
Повторяем попытку...
Скачать видео с ютуб по ссылке или смотреть без блокировок на сайте: 2-Minute Neuroscience: The Hippocampus в качестве 4k
У нас вы можете посмотреть бесплатно 2-Minute Neuroscience: The Hippocampus или скачать в максимальном доступном качестве, видео которое было загружено на ютуб. Для загрузки выберите вариант из формы ниже:
-
Информация по загрузке:
Скачать mp3 с ютуба отдельным файлом. Бесплатный рингтон 2-Minute Neuroscience: The Hippocampus в формате MP3:
Если кнопки скачивания не
загрузились
НАЖМИТЕ ЗДЕСЬ или обновите страницу
Если возникают проблемы со скачиванием видео, пожалуйста напишите в поддержку по адресу внизу
страницы.
Спасибо за использование сервиса ClipSaver.ru
2-Minute Neuroscience: The Hippocampus
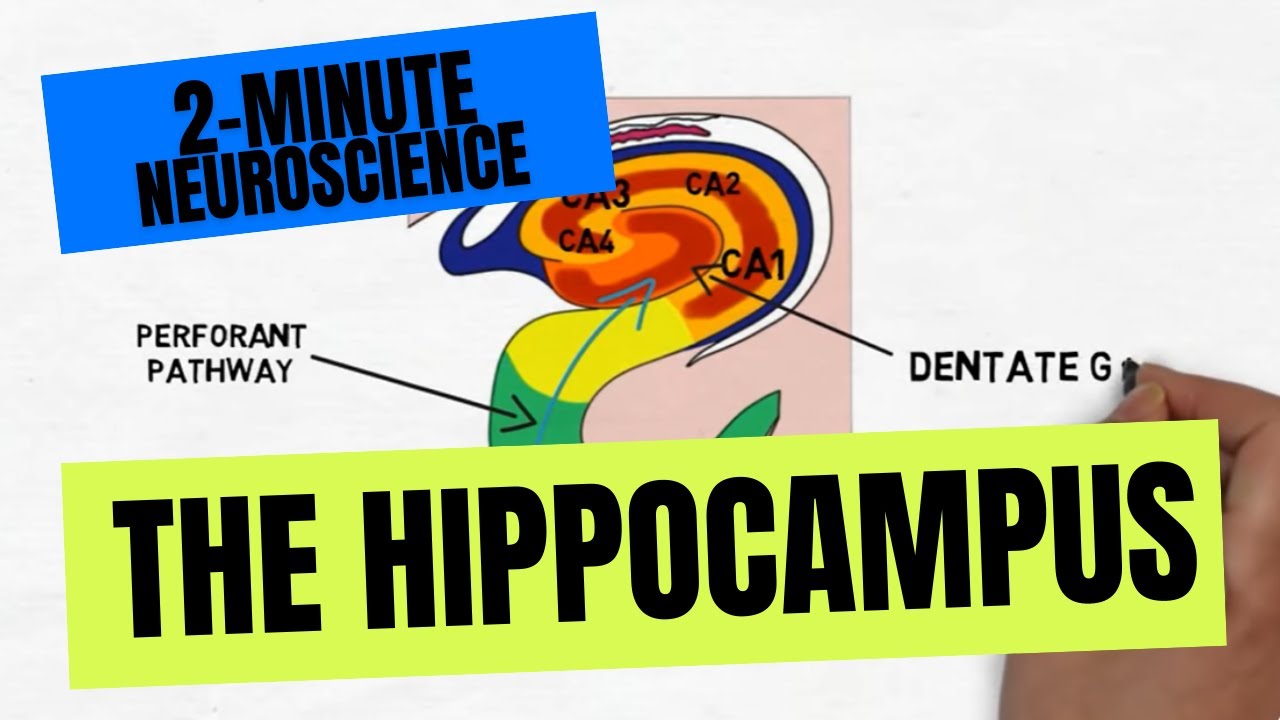
In this video, I cover the structure and function of the hippocampus. I discuss its location in the temporal lobe as well as the other structures that surround it and make up the hippocampal formation, such as the dentate gyrus and hippocampal gyrus. I also describe the flow of information through the hippocampus, starting at the entorhinal cortex and traveling through the dentate gyrus, hippocampus, subiculum, and then to a variety of areas and pathways. For an article (on my website) that explains the hippocampus, click this link: https://neuroscientificallychallenged... If you're looking for accessible and entertaining ways to learn more about the brain, check out my books: 📚Your Brain, Explained: What Neuroscience Reveals About Your Brain and its Quirks: https://www.amazon.com/Your-Brain-Exp... 📚Bizarre: The Most Peculiar Cases of Human Behavior and What They Tell Us About How the Brain Works: https://www.amazon.com/Bizarre-Peculi... TRANSCRIPT: Welcome to 2 minute neuroscience, where I simplistically explain neuroscience topics in 2 minutes or less. In this installment I will discuss the hippocampus. There is a hippocampus in the temporal lobe of each cerebral hemisphere. The name “hippocampus” comes from the Greek for "seahorse" because when it is removed from the brain, it vaguely resembles a seahorse. Although it has many functions, the hippocampus is best known for its role in memory. The hippocampus is part of a larger structure in the temporal lobe called the hippocampal formation. Definitions of what structures are included in the hippocampal formation vary, but generally it is considered to at least include the hippocampus, the adjacent cortex which is called the hippocampal or parahippocampal gyrus, and a strip of gray matter in between the two called the dentate gyrus. The hippocampal gyrus contains areas called the entorhinal cortex and subiculum, which are both involved in the flow of information through the hippocampus. In addition to being compared to a seahorse, the hippocampus has also been likened to the curved horn of a ram or the horns of the ancient Egyptian god ammon and thus has been called Ammon’s horn or cornu ammonis. Accordingly, the hippocampus has been subdivided anatomically into 4 regions designated CA1 through CA4; the CA stands for cornu ammonis. The hippocampus receives information from the rest of the cerebral cortex primarily via the perforant pathway, which originates in the entorhinal cortex and projects to the dentate gyrus. Fibers then leave the dentate gyrus and project to neurons in the CA3 region of the hippocampus; neurons in CA3 then send axons to neurons in the CA1 region, which project to neurons in the subiculum. The subiculum can be considered the main output region of the hippocampal formation; fibers from the subiculum project back upon neurons in the entorhinal cortex and then fibers from the entorhinal cortex travel out to a variety of areas in the cerebrum. Output fibers also leave the subiculum and hippocampus and enter the fornix, a fiber bundle that connects the hippocampus with a variety of subcortical areas like the thalamus and hypothalamus. Reference: Purves D, Augustine GJ, Fitzpatrick D, Hall WC, Lamantia AS, McNamara JO, White LE. Neuroscience. 4th ed. Sunderland, MA. Sinauer Associates; 2008.



















