Van Der Waal's Equation of Real Gases Part II (Urdu/Hindi/English) скачать в хорошем качестве
van der waals equation
van der waals equation for real gases
van der waals equation of state
van der waals equation explained
van der waals gas equation
van der waals equation in hindi
van der waal's equation
van der waals equation derivation
van der waals equation in chemistry
real gas equation
van der waals
derivation of van der waals equation
volume correction in van der waals equation
equation
van der waals equation of state for real gases
Повторяем попытку...
Скачать видео с ютуб по ссылке или смотреть без блокировок на сайте: Van Der Waal's Equation of Real Gases Part II (Urdu/Hindi/English) в качестве 4k
У нас вы можете посмотреть бесплатно Van Der Waal's Equation of Real Gases Part II (Urdu/Hindi/English) или скачать в максимальном доступном качестве, видео которое было загружено на ютуб. Для загрузки выберите вариант из формы ниже:
-
Информация по загрузке:
Скачать mp3 с ютуба отдельным файлом. Бесплатный рингтон Van Der Waal's Equation of Real Gases Part II (Urdu/Hindi/English) в формате MP3:
Если кнопки скачивания не
загрузились
НАЖМИТЕ ЗДЕСЬ или обновите страницу
Если возникают проблемы со скачиванием видео, пожалуйста напишите в поддержку по адресу внизу
страницы.
Спасибо за использование сервиса ClipSaver.ru
Van Der Waal's Equation of Real Gases Part II (Urdu/Hindi/English)
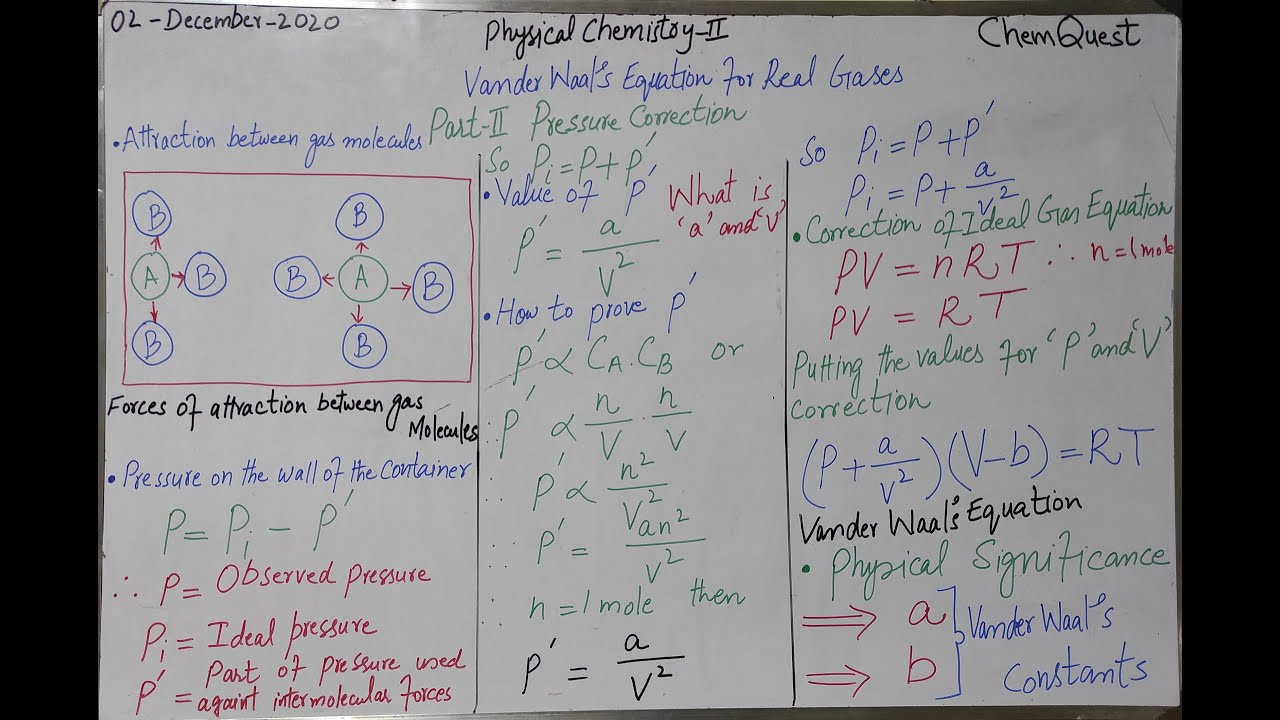
#ChemQuest #Teaching #PhysicalChemistryII In this lecture Vander Waal's Equation "Pressure Correction" is given in detail. Van Der Waal's Equation, Volume Correction Part I (Urdu/Hindi/English) • Van Der Waal's Equation, Volume Correction... According to the ideal gas law, PV = nRT, where P is the pressure, V is the volume, n is the number of moles, T is the temperature, and R is the universal gas constant. The Van der Waals equation is also known as the Van der Waals equation of state for real gases which do not follow ideal gas law. In chemistry and thermodynamics, the Van der Waals equation (or Van der Waals equation of state) is an equation of state which extends the ideal gas law to include the effects of interaction between molecules of a gas, as well as accounting for the finite size of the molecules. The ideal gas law treats gas molecules as point particles that interact with their containers but not each other, meaning they neither take up space nor change kinetic energy during collisions (i.e. all collisions are perfectly elastic). The ideal gas law states that the volume V occupied by n moles of any gas has a pressure P at temperature T given by the following relationship, where R is the gas constant: {\displaystyle PV=nRT}PV=nRT To account for the volume occupied by real gas molecules, the Van der Waals equation replaces {\displaystyle V/n}V/n in the ideal gas law with {\displaystyle (V_{m}-b)}{\displaystyle (V_{m}-b)}, where Vm is the molar volume of the gas and b is the volume occupied by the molecules of one mole: {\displaystyle P(V_{m}-b)=RT}{\displaystyle P(V_{m}-b)=RT} Van der Waals equation on a wall in Leiden The second modification made to the ideal gas law accounts for interaction between molecules of the gas. The Van der Waals equation includes intermolecular interaction by adding to the observed pressure P in the equation of state a term of the form {\displaystyle a/V_{m}^{2}}{\displaystyle a/V_{m}^{2}}, where a is a constant whose value depends on the gas.



















