Скачать с ютуб Achilles Tendon Stress & Strain - Everything You Need To Know - Dr. Nabil Ebraheim в хорошем качестве
Achilles
tendon
rupture
stress
strain
watershed
zone
vascularity
weekend
warrior
injury
calcaneal
insertion
bursa
subcutaneous
subtendinous
Dr. Nabil Ebraheim
Nathan Elkins
UTMC
orthopaedics
UT surgeon
molly
Thompson's
test
gastrocnemius
soleus
lower
leg
muscles
calcaneus
ankle
squeeze
calf
intact
ruptured
surgeon
Скачать бесплатно и смотреть ютуб-видео без блокировок Achilles Tendon Stress & Strain - Everything You Need To Know - Dr. Nabil Ebraheim в качестве 4к (2к / 1080p)
У нас вы можете посмотреть бесплатно Achilles Tendon Stress & Strain - Everything You Need To Know - Dr. Nabil Ebraheim или скачать в максимальном доступном качестве, которое было загружено на ютуб. Для скачивания выберите вариант из формы ниже:
Загрузить музыку / рингтон Achilles Tendon Stress & Strain - Everything You Need To Know - Dr. Nabil Ebraheim в формате MP3:
Если кнопки скачивания не
загрузились
НАЖМИТЕ ЗДЕСЬ или обновите страницу
Если возникают проблемы со скачиванием, пожалуйста напишите в поддержку по адресу внизу
страницы.
Спасибо за использование сервиса ClipSaver.ru
Achilles Tendon Stress & Strain - Everything You Need To Know - Dr. Nabil Ebraheim
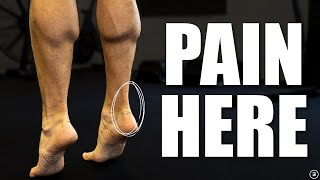
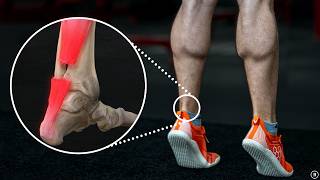
Dr. Ebraheim’s educational animated video describes the anatomy of Achilles tendon. Anatomy of the Achilles tendon. The Achilles tendon is located in the posterior ankle. The Achilles tendon is the strongest and thickest tendon in the body. It is formed from the soleus and gastrocnemius muscles. The Achilles tendon is inserted into the calcaneus bone. The subcutaneous calcaneal bursa is found superficial to the Achilles tendon. The bursa lies between the skin and the distal aspect of the Achilles tendon. There is also a subtendinous calcaneal bursa located deep to the Achilles tendon. This bursa is located between the Achilles tendon and the calcaneal bone. Inflammation of one or both of this bursa can cause pain in the posterior heel or ankle. The Achilles tendon is prone to tear or rupture and most of the ruptures occur above the calcaneal insertion of the tendon. Like all tendons the Achilles tendon doesn’t have great vascularity. The watershed zone is a part of the tendon that has the worst blood supply. This is a narrow area in width between 2-6 cm proximal to the calcaneus. The Achilles tendon is prone to tendonitis or tendon rupture in this area due to limited blood supply. When the Achilles tendon ruptures within this area, the result may be similar to pulling rope. This injury is also referred to as the weaken warriors injury. The injury typically occurs if over performing or overdoing a physical activity. The injury also occurs more in men aged 30-40 years. The mechanism of injury for rupture of the Achilles is usually from an eccentric load on a dorsiflexed ankle with knee extension. The strain placed on the tendon less than 4% is within the normal limits of the physiological load. The fibers return to the original configuration when the load is removed. Starin between 4-8% lead to microscopic failure. Starin beyond 8% results in macroscopic failure and rupture of the Achilles tendon. The Thompson test is performed in order to make a diagnosis of Achilles tendon tear. Become a friend on facebook: / drebraheim Follow me on twitter: https://twitter.com/#!/DrEbraheim_UTMC