Скачать с ютуб Who Were the Franks? The Story of a Germanic Tribe That Changed History в хорошем качестве
#HistoryExplained
#MedievalHistory
#AncientHistory
#HistoricalFacts
#EuropeanHistory
#WorldHistory
#TheFranks
#Merovingians
#Carolingians
#RiseOfCharlemagne
#HolyRomanEmpire
#FrankishEmpire
#BattleOfTours
#ClovisTheGreat
#CharlemagneLegacy
#FrankishKingdom
#DarkAges
#MedievalEurope
#Christianization
#RomanEmpireFall
#BarbarianTribes
#GermanicPeoples
Скачать бесплатно и смотреть ютуб-видео без блокировок Who Were the Franks? The Story of a Germanic Tribe That Changed History в качестве 4к (2к / 1080p)
У нас вы можете посмотреть бесплатно Who Were the Franks? The Story of a Germanic Tribe That Changed History или скачать в максимальном доступном качестве, которое было загружено на ютуб. Для скачивания выберите вариант из формы ниже:
Загрузить музыку / рингтон Who Were the Franks? The Story of a Germanic Tribe That Changed History в формате MP3:
Если кнопки скачивания не
загрузились
НАЖМИТЕ ЗДЕСЬ или обновите страницу
Если возникают проблемы со скачиванием, пожалуйста напишите в поддержку по адресу внизу
страницы.
Спасибо за использование сервиса ClipSaver.ru
Who Were the Franks? The Story of a Germanic Tribe That Changed History
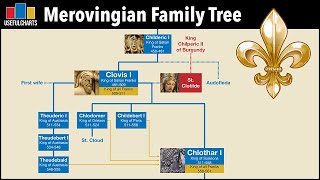
Franks were a Germanic people whose rise to prominence shaped the history of medieval Europe. Originating in the lower Rhine region during the late Roman period, the Franks established one of the most powerful and enduring kingdoms in Western Europe. Through their political unity, military successes, and cultural contributions, the Franks laid the groundwork for the medieval European order and influenced the course of history. Origins and Early History The Franks first appeared in historical records during the 3rd century CE as a confederation of Germanic tribes living along the lower Rhine River. They were initially semi-nomadic, known for their warrior culture and frequent raids on Roman territories. Over time, some Franks were integrated into the Roman military, serving as foederati (allied troops) and settling within the Roman Empire. By the 5th century, as the Western Roman Empire collapsed, the Franks expanded their territory under the leadership of chieftains like Childeric I, a member of the Merovingian dynasty. Clovis I and the Birth of the Frankish Kingdom The true consolidation of Frankish power began under Clovis I (r. 481–511), a pivotal figure in the tribe's history. Clovis unified the various Frankish tribes through warfare and diplomacy, creating a centralized kingdom that spanned much of modern-day France and parts of Germany. One of the most significant events during Clovis's reign was his conversion to Christianity, likely influenced by his wife, Clotilde, who was a devout Catholic. Clovis's baptism around 496 CE marked the beginning of a strong alliance between the Frankish monarchy and the Catholic Church. This alliance bolstered the legitimacy of his rule and facilitated the Christianization of his subjects. The Merovingians and Carolingians Under the Merovingian dynasty, the Franks established a tradition of governance that combined Roman administrative practices with Germanic tribal customs. However, by the 7th century, Merovingian kings became figureheads, with real power shifting to the mayors of the palace—administrative officials who acted as regents. This shift in power culminated in the rise of the Carolingian dynasty. In 751, Pepin the Short, a mayor of the palace, deposed the last Merovingian king and was crowned king of the Franks with the approval of the pope. Pepin's son, Charlemagne (r. 768–814), became one of the most famous rulers in European history, leading the Carolingian Empire to unprecedented heights. Charlemagne and the Frankish Legacy Charlemagne expanded the Frankish kingdom into an empire that included much of Western and Central Europe. In 800 CE, he was crowned Emperor of the Romans by Pope Leo III, marking the revival of the Western Roman Empire and the foundation of the Holy Roman Empire. Charlemagne's reign was a golden age for the Franks. He implemented administrative reforms, promoted education and cultural revival (the Carolingian Renaissance), and supported the spread of Christianity across his empire. The Frankish Empire became a model for medieval European governance and culture. Decline and Fragmentation After Charlemagne’s death, the Frankish Empire was divided among his heirs, leading to internal conflicts and the eventual fragmentation of the empire. The Treaty of Verdun in 843 divided the empire into three parts, laying the foundations for the modern states of France, Germany, and Italy. Although the Frankish political unity dissolved, their legacy endured. The Frankish legal and cultural traditions, combined with their role in spreading Christianity, significantly influenced the development of medieval Europe. Cultural and Historical Impact The Franks were instrumental in transitioning Europe from the ancient world to the medieval era. Their adoption of Christianity, alliance with the papacy, and establishment of feudal governance became hallmarks of medieval European society. The Frankish legacy is especially evident in modern France, whose name derives from the Franks. #Franks, #Merovingians, #Carolingians, #RiseOfCharlemagne, #HolyRomanEmpire, #FrankishEmpire, #BattleOfTours







![Avenging Varus - The Germanic Wars [FULL DOCUMENTARY]](https://i.ytimg.com/vi/ZyzY4ayG8R4/mqdefault.jpg)
