Investigating the Proportion of Electric Cars in Two Populations скачать в хорошем качестве
Повторяем попытку...
Скачать видео с ютуб по ссылке или смотреть без блокировок на сайте: Investigating the Proportion of Electric Cars in Two Populations в качестве 4k
У нас вы можете посмотреть бесплатно Investigating the Proportion of Electric Cars in Two Populations или скачать в максимальном доступном качестве, видео которое было загружено на ютуб. Для загрузки выберите вариант из формы ниже:
-
Информация по загрузке:
Скачать mp3 с ютуба отдельным файлом. Бесплатный рингтон Investigating the Proportion of Electric Cars in Two Populations в формате MP3:
Если кнопки скачивания не
загрузились
НАЖМИТЕ ЗДЕСЬ или обновите страницу
Если возникают проблемы со скачиванием видео, пожалуйста напишите в поддержку по адресу внизу
страницы.
Спасибо за использование сервиса ClipSaver.ru
Investigating the Proportion of Electric Cars in Two Populations
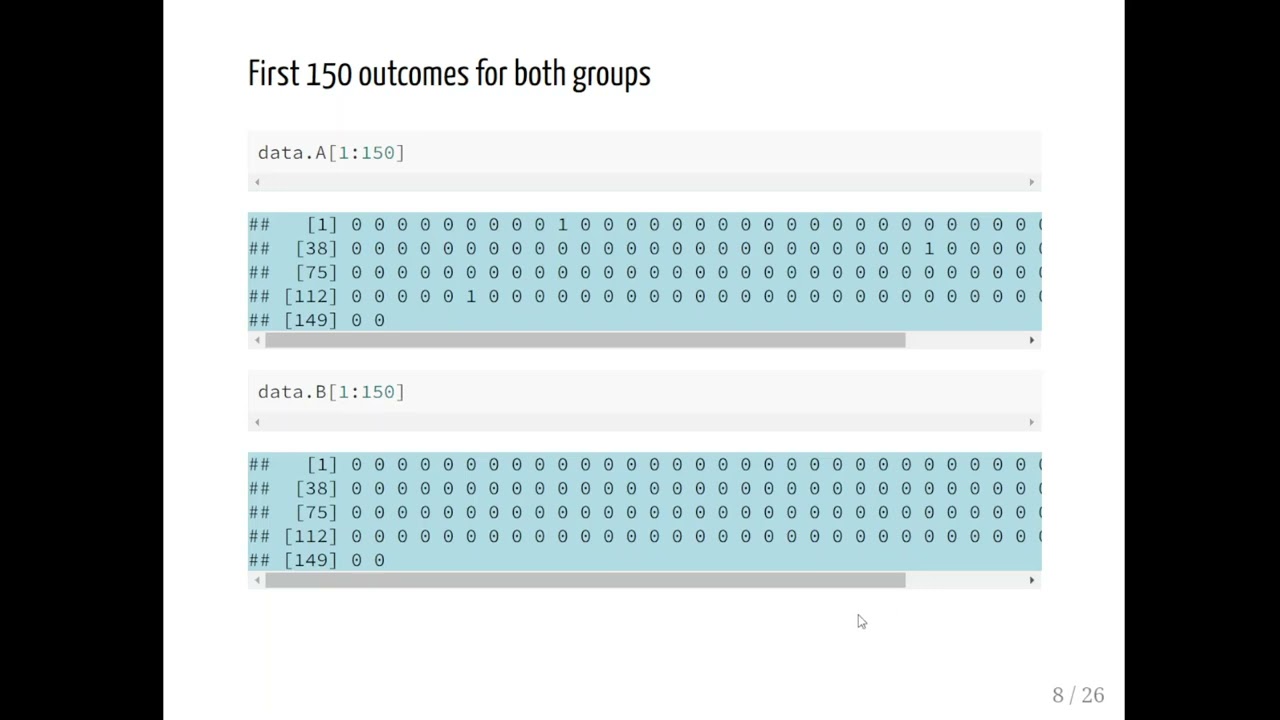
Investigating the Proportion of Electric Cars in Two Populations This exercise involves simulating data, estimating confidence intervals, and performing hypothesis testing to investigate the proportion of electric cars among registered cars in two large populations (A and B). A researcher wants to investigate the proportion of electric cars among all registered cars in two large populations (denoted as populations A and B). Two samples are considered, one from each population. The first sample consists of n_A = 900 registered cars, while the second sample consists of n_B = 1,200 registered cars. The type of each car (electric or not) is assumed to be independent of the type of other cars in the samples. *A.* Simulate the two samples in R assuming that the proportion of electric cars in population A is 0.02, while in population B it is 0.025, and save the simulated samples for later use. *B.* The true proportions of electric cars in the two populations are unknown to the researcher, and the researcher wants to estimate them. Determine an equal-tailed 99% confidence interval for the difference in the true proportions of electric cars in the two populations A and B, using your sample data. *C.* Based on previous knowledge, the researcher believes that the proportion of electric cars in population A is lower than the proportion of electric cars in population B. Perform a hypothesis test to investigate this belief using your sample data. In doing so, you should include the following steps, in addition to any other necessary steps: Compute the value of a suitable test statistic under an appropriate normal approximation. Compute the p-value of the test. State your conclusion based on the calculated p-value.















![Доверительный интервал [Простое объяснение]](https://image.4k-video.ru/id-video/ENnlSlvQHO0)



