Understanding Copy Elision and Return Value Optimization in C++ скачать в хорошем качестве
Повторяем попытку...

Скачать видео с ютуб по ссылке или смотреть без блокировок на сайте: Understanding Copy Elision and Return Value Optimization in C++ в качестве 4k
У нас вы можете посмотреть бесплатно Understanding Copy Elision and Return Value Optimization in C++ или скачать в максимальном доступном качестве, видео которое было загружено на ютуб. Для загрузки выберите вариант из формы ниже:
-
Информация по загрузке:
Скачать mp3 с ютуба отдельным файлом. Бесплатный рингтон Understanding Copy Elision and Return Value Optimization in C++ в формате MP3:
Если кнопки скачивания не
загрузились
НАЖМИТЕ ЗДЕСЬ или обновите страницу
Если возникают проблемы со скачиванием видео, пожалуйста напишите в поддержку по адресу внизу
страницы.
Спасибо за использование сервиса ClipSaver.ru
Understanding Copy Elision and Return Value Optimization in C++
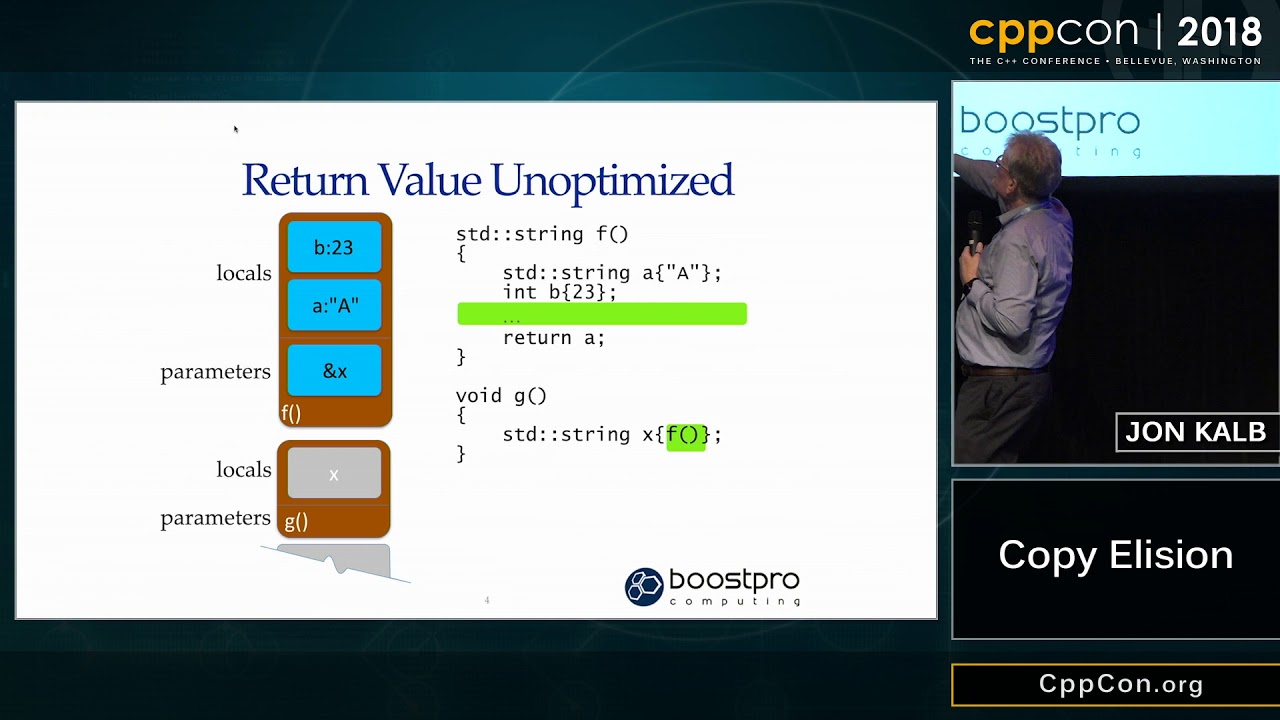
Discover the concepts of copy elision and return value optimization (RVO) in C++. Learn how these techniques enhance performance by eliminating unnecessary copying of objects. --- Disclaimer/Disclosure: Some of the content was synthetically produced using various Generative AI (artificial intelligence) tools; so, there may be inaccuracies or misleading information present in the video. Please consider this before relying on the content to make any decisions or take any actions etc. If you still have any concerns, please feel free to write them in a comment. Thank you. --- In the world of C++, performance is paramount. Two key techniques that contribute significantly to performance optimization are copy elision and return value optimization (RVO). These techniques help minimize the overhead associated with copying objects, ensuring more efficient execution of programs. Let's dive into what these concepts entail and how they impact C++ programming. Copy Elision Copy elision is a compiler optimization technique that eliminates unnecessary copying of objects. In C++, creating and destroying temporary objects can be expensive, especially if these objects are complex or large. Copy elision aims to optimize this by eliminating the creation of temporary objects in certain situations. This optimization is permitted and often performed by the compiler, even if the object's copy constructor or move constructor has side effects. Examples of Copy Elision Named Return Value Optimization (NRVO): [[See Video to Reveal this Text or Code Snippet]] In this example, the compiler can optimize away the copy of obj when returning it from the createObject function. Instead of creating a temporary copy, the compiler constructs the return value directly in the location where the caller expects it. Temporary Objects: [[See Video to Reveal this Text or Code Snippet]] Here, the compiler can eliminate the temporary object creation by constructing obj directly. Return Value Optimization (RVO) Return value optimization (RVO) is a specific form of copy elision that occurs when a function returns a temporary object. RVO allows the compiler to construct the return value directly in the memory location where it would be used, thus avoiding an unnecessary copy or move operation. Example of RVO [[See Video to Reveal this Text or Code Snippet]] In this case, the temporary object created by MyClass() is constructed directly in the memory location designated for the return value, avoiding a copy or move. Benefits of Copy Elision and RVO Performance Improvement: By eliminating unnecessary copies, both copy elision and RVO reduce the overhead associated with object creation and destruction, leading to faster code execution. Resource Efficiency: Reducing the number of temporary objects lowers memory usage and can help avoid potential resource contention issues. Cleaner Code: These optimizations allow developers to write cleaner, more intuitive code without worrying about the performance penalties of copying objects. Guaranteed Copy Elision in C++17 With the introduction of C17, copy elision became mandatory in certain situations, making these optimizations more predictable and reliable. Specifically, C17 requires copy elision in the following scenarios: When a temporary object is returned from a function. When a temporary object is thrown and caught by exception handling. This guarantee ensures that developers can rely on copy elision to avoid unnecessary copies, leading to more efficient and performant code. Conclusion Copy elision and return value optimization are powerful techniques in C++ that enhance performance by eliminating unnecessary object copying. By understanding and leveraging these optimizations, developers can write more efficient and effective code. With the mandatory copy elision introduced in C++17, these optimizations have become even more reliable, helping to simplify code and improve performance.





![Как происходит модернизация остаточных соединений [mHC]](https://imager.clipsaver.ru/jYn_1PpRzxI/max.jpg)