Скачать с ютуб Rheumatic Fever Symptoms, Treatment, and Causes в хорошем качестве
Rheumatic Fever
Heart Disease
Streptococcal Infections
Autoimmune Disease
Rheumatic Heart Disease
Heart Health
Symptoms
Causes
Treatment
Prevention
Cardiology
Autoimmune Disorders
Heart Valve Damage
Rheumatology
Infectious Diseases
Group A Streptococcus
Scarlet Fever
Inflammation
Antibiotics
Pediatric Health
Rheumatic Fever Awareness
Heart Complications
Heart Valve Repair
Medical Conditions
Health Education.
Скачать бесплатно и смотреть ютуб-видео без блокировок Rheumatic Fever Symptoms, Treatment, and Causes в качестве 4к (2к / 1080p)
У нас вы можете посмотреть бесплатно Rheumatic Fever Symptoms, Treatment, and Causes или скачать в максимальном доступном качестве, которое было загружено на ютуб. Для скачивания выберите вариант из формы ниже:
Загрузить музыку / рингтон Rheumatic Fever Symptoms, Treatment, and Causes в формате MP3:
Если кнопки скачивания не
загрузились
НАЖМИТЕ ЗДЕСЬ или обновите страницу
Если возникают проблемы со скачиванием, пожалуйста напишите в поддержку по адресу внизу
страницы.
Спасибо за использование сервиса savevideohd.ru
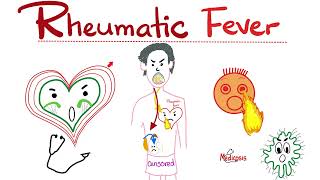
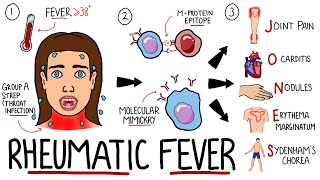
Rheumatic Fever Symptoms, Treatment, and Causes
Rheumatic fever is an inflammatory disease that can develop as a complication of untreated or inadequately treated streptococcal throat infections, particularly those caused by group A streptococcus bacteria (Streptococcus pyogenes). It primarily affects the connective tissues of the heart, joints, skin, and brain. The condition is more common in children and young adults and can lead to serious health complications if not properly managed. Here are some key points about rheumatic fever: 1. Causes and Triggers: Rheumatic fever is triggered by an immune response to the streptococcal bacteria that cause strep throat. In some individuals, the immune system mistakenly targets and attacks healthy tissues in the body, leading to inflammation and damage. Not everyone who gets a strep infection will develop rheumatic fever, and there may be genetic factors that influence susceptibility. 2. Symptoms: The symptoms of rheumatic fever can vary and may include: Fever Joint pain and swelling (arthritis), especially in the larger joints like the knees, elbows, ankles, and wrists Chest pain and heart palpitations Skin rash Chorea (involuntary jerky movements) Fatigue Shortness of breath 3. Heart Involvement: One of the most serious consequences of rheumatic fever is damage to the heart valves. This can lead to a condition known as rheumatic heart disease. The heart valves may become scarred and less functional, affecting blood flow and potentially leading to heart murmurs, heart failure, and other cardiovascular complications. 4. Diagnosis: Diagnosis of rheumatic fever is based on a combination of clinical symptoms, medical history, and laboratory tests. Doctors may look for evidence of recent streptococcal infection through throat swabs or blood tests, and they may also use criteria established by medical organizations to confirm the diagnosis. 5. Treatment: The primary treatment for rheumatic fever involves targeting the underlying streptococcal infection with antibiotics, usually penicillin or other suitable antibiotics if the patient is allergic to penicillin. Inflammation and symptoms are often managed with anti-inflammatory medications such as nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs) or corticosteroids. Long-term treatment may be necessary to prevent further heart valve damage and complications. 6. Prevention: Preventing rheumatic fever involves promptly and effectively treating strep throat infections with appropriate antibiotics. Timely treatment of strep throat can greatly reduce the risk of developing rheumatic fever. In some cases, individuals with a history of rheumatic fever may need to take preventive antibiotics for a period of time to prevent recurrent infections. 7. Complications: If left untreated or not managed properly, rheumatic fever can lead to serious complications, including rheumatic heart disease, heart valve damage, heart failure, and an increased risk of stroke. It's important to note that rheumatic fever has become less common in many developed countries due to improved hygiene, access to healthcare, and the use of antibiotics to treat streptococcal infections. However, it still remains a significant health concern in certain regions with limited access to medical care. If you suspect you or someone else has symptoms of rheumatic fever, it's crucial to seek medical attention promptly.