Как болезнь Альцгеймера влияет на клетки вашего мозга скачать в хорошем качестве
Повторяем попытку...
Скачать видео с ютуб по ссылке или смотреть без блокировок на сайте: Как болезнь Альцгеймера влияет на клетки вашего мозга в качестве 4k
У нас вы можете посмотреть бесплатно Как болезнь Альцгеймера влияет на клетки вашего мозга или скачать в максимальном доступном качестве, видео которое было загружено на ютуб. Для загрузки выберите вариант из формы ниже:
-
Информация по загрузке:
Скачать mp3 с ютуба отдельным файлом. Бесплатный рингтон Как болезнь Альцгеймера влияет на клетки вашего мозга в формате MP3:
Если кнопки скачивания не
загрузились
НАЖМИТЕ ЗДЕСЬ или обновите страницу
Если возникают проблемы со скачиванием видео, пожалуйста напишите в поддержку по адресу внизу
страницы.
Спасибо за использование сервиса ClipSaver.ru
Как болезнь Альцгеймера влияет на клетки вашего мозга
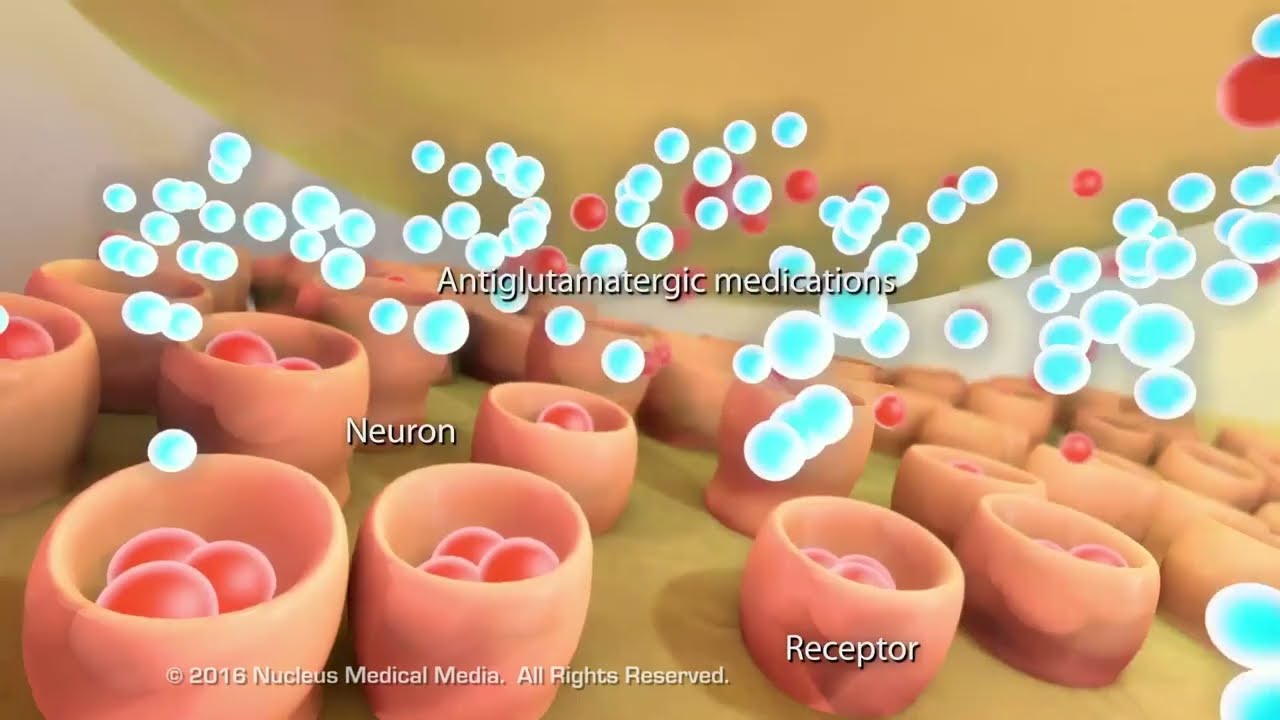
СТЕНОГРАММА МЕДИЦИНСКОЙ АНИМАЦИИ: Когнитивные функции мозга включают память, то есть процесс сохранения и извлечения информации. Воспоминания формируются в гиппокампе, состоящем из нейронов, обрабатывающих информацию. Каждый нейрон получает химические сигналы от других нейронов через дендриты, а затем преобразует их в электрический заряд, называемый потенциалом действия. В пространстве между ними нейроны выделяют стимулирующие химические вещества, называемые нейротрансмиттерами, которые связываются с рецепторами принимающей клетки и передают информацию. Болезнь Альцгеймера — это постепенное дегенеративное заболевание мозга, при котором нейроны памяти и других когнитивных областей мозга теряют функцию и погибают, что приводит сначала к прогрессирующей потере памяти, затем к трудностям в обучении и общении, и, в конечном итоге, к нарушению основных функций, таких как дыхание. В здоровых нейронах ферменты помогают перерабатывать белок, называемый белком-предшественником амилоида, во фрагменты, которые способствуют нормальному функционированию клеток. При болезни Альцгеймера аномальная ферментативная обработка приводит к образованию фрагментов, включающих липкий пептид, называемый бета-амилоидом. Бета-амилоид накапливается во внеклеточном пространстве, образуя скопления, называемые амилоидными бляшками. Эти скопления блокируют электрические и химические связи между нейронами. Внутри здоровых нейронов микротрубочки и тау-белки образуют упорядоченную структуру, которая переносит ионы и питательные вещества внутрь клетки. При болезни Альцгеймера химические изменения внутри нейронов повреждают тау-белок, аномально скручивая микротрубочки в нейрофибриллярные клубки, что нарушает доставку ионов и питательных веществ внутрь клетки. По мере размножения бляшек и клубков в мозговой ткани нейронные связи ослабевают, а истощенные клетки теряют функцию, что приводит к обширной гибели нейронов, уменьшению массы мозга и тяжелым когнитивным и функциональным нарушениям. Лекарства от болезни Альцгеймера не существует, но современные методы лечения включают ингибиторы холинэстеразы, которые замедляют распад ацетилхолина, нейромедиатора, важного для памяти и обучения, и антиглутаматергические препараты, которые регулируют активность глутамата, другого нейромедиатора, необходимого для памяти и обучения, блокируя чрезмерное связывание глутамата с нейронами, тем самым предотвращая дисфункцию и гибель нейронов. ♪ [музыка] ♪ #БолезньАльцгеймера #ПотеряПамять #КлеткиМозга ANM11034