Intracerebral hemorrhage (mechanism of disease) скачать в хорошем качестве
Повторяем попытку...
Скачать видео с ютуб по ссылке или смотреть без блокировок на сайте: Intracerebral hemorrhage (mechanism of disease) в качестве 4k
У нас вы можете посмотреть бесплатно Intracerebral hemorrhage (mechanism of disease) или скачать в максимальном доступном качестве, видео которое было загружено на ютуб. Для загрузки выберите вариант из формы ниже:
-
Информация по загрузке:
Скачать mp3 с ютуба отдельным файлом. Бесплатный рингтон Intracerebral hemorrhage (mechanism of disease) в формате MP3:
Если кнопки скачивания не
загрузились
НАЖМИТЕ ЗДЕСЬ или обновите страницу
Если возникают проблемы со скачиванием видео, пожалуйста напишите в поддержку по адресу внизу
страницы.
Спасибо за использование сервиса ClipSaver.ru
Intracerebral hemorrhage (mechanism of disease)
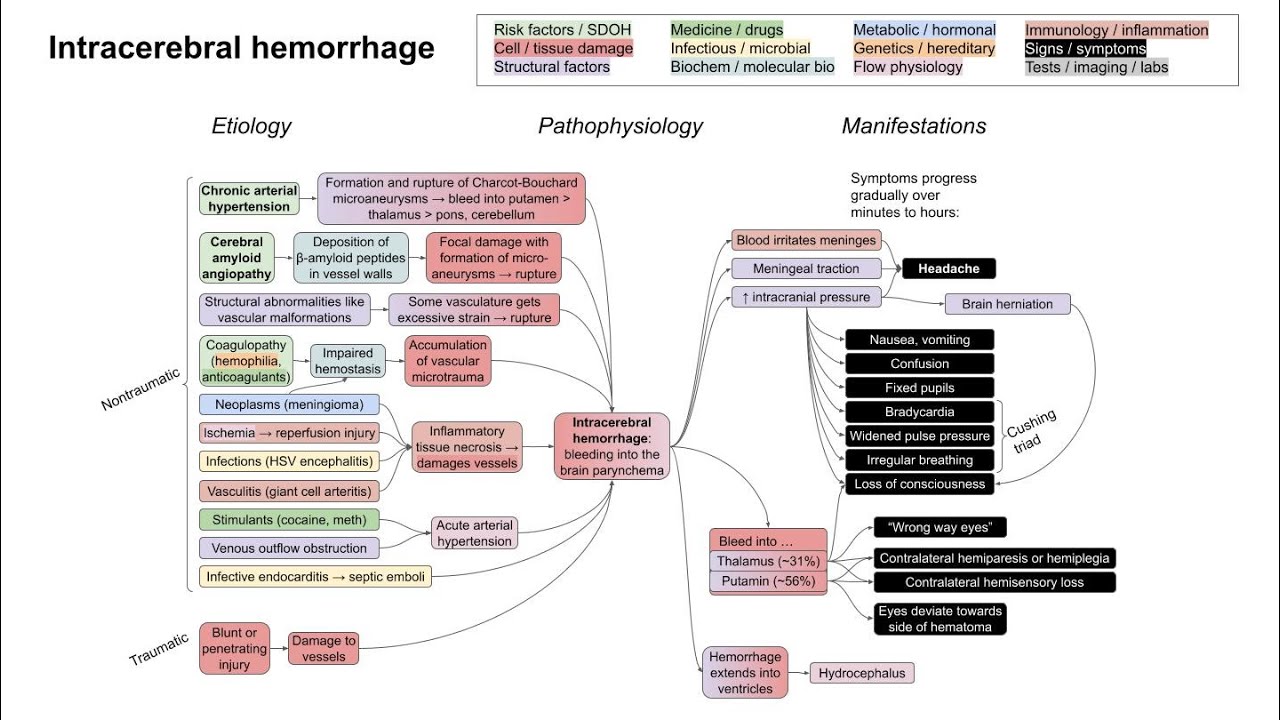
This is a flowchart on intracerebral hemorrhage, covering the etiology, pathophysiology, and manifestations. ADDITIONAL TAGS: Bleed into … Putamin (~56%) Neoplasms (meningioma) Risk factors / SDOH Cell / tissue damage Structural factors Intracerebral hemorrhage Medicine / drugs Infectious / microbial Biochem / molecular bio Immunology / inflammation Signs / symptoms Tests / imaging / labs Metabolic / hormonal Genetics / hereditary Flow physiology Pathophysiology Etiology Manifestations Intracerebral hemorrhage: bleeding into the brain parynchema Blunt or penetrating injury Chronic arterial hypertension Traumatic Nontraumatic Damage to vessels Formation and rupture of Charcot-Bouchard microaneurysms → bleed into putamen thalamus pons, cerebellum Cerebral amyloid angiopathy Deposition of β-amyloid peptides in vessel walls Focal damage with formation of micro- aneurysms → rupture Structural abnormalities like vascular malformations Some vasculature gets excessive strain → rupture Coagulopathy (hemophilia, anticoagulants) Impaired hemostasis Accumulation of vascular microtrauma Inflammatory tissue necrosis → damages vessels Infections (HSV encephalitis) Ischemia → reperfusion injury Acute arterial hypertension Venous outflow obstruction Stimulants (cocaine, meth) Vasculitis (giant cell arteritis) Infective endocarditis → septic emboli Blood irritates meninges Meningeal traction ↑ intracranial pressure Headache Nausea, vomiting Confusion Fixed pupils Bradycardia Loss of consciousness Thalamus (~31%) Contralateral hemiparesis or hemiplegia Contralateral hemisensory loss Eyes deviate towards side of hematoma “Wrong way eyes” Hemorrhage extends into ventricles Hydrocephalus Brain herniation Widened pulse pressure Irregular breathing Cushing triad Symptoms progress gradually over minutes to hours