Brachial Plexus anatomy and branches скачать в хорошем качестве
Повторяем попытку...
Скачать видео с ютуб по ссылке или смотреть без блокировок на сайте: Brachial Plexus anatomy and branches в качестве 4k
У нас вы можете посмотреть бесплатно Brachial Plexus anatomy and branches или скачать в максимальном доступном качестве, видео которое было загружено на ютуб. Для загрузки выберите вариант из формы ниже:
-
Информация по загрузке:
Скачать mp3 с ютуба отдельным файлом. Бесплатный рингтон Brachial Plexus anatomy and branches в формате MP3:
Если кнопки скачивания не
загрузились
НАЖМИТЕ ЗДЕСЬ или обновите страницу
Если возникают проблемы со скачиванием видео, пожалуйста напишите в поддержку по адресу внизу
страницы.
Спасибо за использование сервиса ClipSaver.ru
Brachial Plexus anatomy and branches
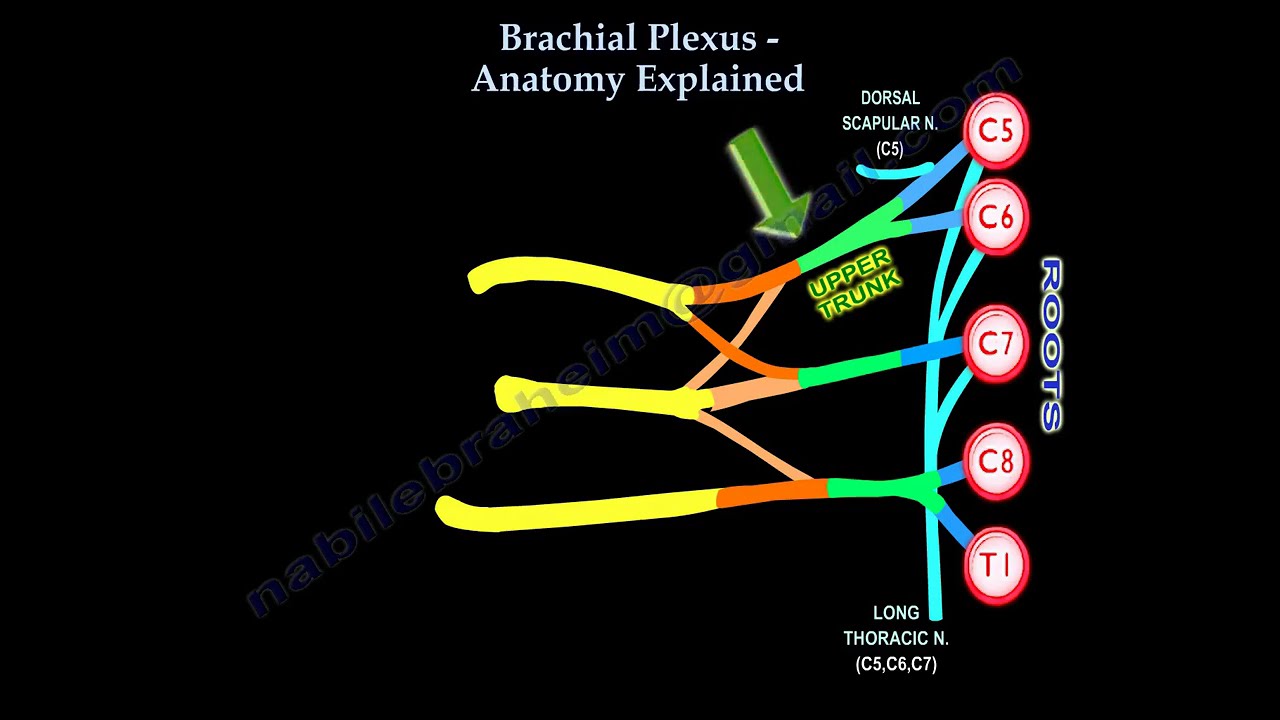
Join this channel to support the channel / @nabilebraheim Brachial Plexus anatomy and branches overview The brachial plexus has 5 roots: C5, C6, C7, C8, and T1. These roots combine to form trunks, divisions, cords, and branches as follows: The upper trunk is formed by the union of C5 and C6. The middle trunk is formed by C7. The lower trunk is formed by the union of C8 and T1. Each trunk then splits into two divisions: Anterior division Posterior division These divisions reorganize into three cords: The three posterior divisions unite to form the Posterior cord. The upper two anterior divisions join to form the Lateral cord. The anterior division of the lower trunk forms the Medial cord. These cords are named based on their position relative to the Axillary artery. Branches of the Brachial Plexus From the Roots: C5 gives rise to: Dorsal scapular nerve, which supplies the following muscles: Levator scapula muscle Rhomboid major muscle Rhomboid minor muscle C5, C6, and C7 together form the Long thoracic nerve, which supplies the Serratus anterior muscle. Injury to this nerve leads to weakness in the serratus anterior, causing medial winging of the scapula. In cases of brachial plexus injury with medial scapular winging, it's important to determine whether the injury is preganglionic or postganglionic. Look for associated conditions like Horner’s syndrome (ptosis, miosis, anhidrosis, enophthalmos), which are indicative of a preganglionic lesion. Upper trunk gives rise to: Suprascapular nerve, which supplies: Supraspinatus muscle Infraspinatus muscle Nerve to subclavius, which supplies the subclavius muscle. Divisions: The divisions (anterior and posterior) do not give off any branches. From the Lateral Cord: Lateral pectoral nerve, which innervates the pectoralis major (clavicular head). Musculocutaneous nerve, which innervates the coracobrachialis, biceps brachii, and brachialis muscles. Lateral branch of the median nerve, which contributes to the innervation of the flexor muscles in the forearm and parts of the hand. From the Posterior Cord: Upper subscapular nerve, which innervates the subscapularis muscle. Thoracodorsal nerve, which innervates the latissimus dorsi muscle. Lower subscapular nerve, which innervates: Subscapularis muscle Teres major muscle Axillary nerve, which innervates: Deltoid muscle Teres minor muscle Radial nerve, which supplies the triceps brachii, brachioradialis, and extensor muscles of the forearm, as well as sensation to the posterior arm, forearm, and dorsum of the hand. From the Medial Cord: Medial pectoral nerve, which innervates the pectoralis major (sternal head) and pectoralis minor muscles. Medial cutaneous nerve of the arm, which provides sensory innervation to the skin on the medial aspect of the arm. Medial cutaneous nerve of the forearm (Medial antibrachial nerve), which provides sensory innervation to the skin on the medial forearm. Ulnar nerve, which innervates: Flexor carpi ulnaris and half of the flexor digitorum profundus in the forearm Most intrinsic muscles of the hand, including the lumbricals, interossei, and thenar muscles (except for the opponens pollicis, abductor pollicis brevis, and flexor pollicis brevis). Medial branch of the median nerve, which supplies some muscles in the forearm and hand. Quiz 1: Which roots combine to form the upper trunk of the brachial plexus? ✔️ C5 and C6 C7 and C8 C6 and C7 C8 and T1 Explanation: The upper trunk of the brachial plexus is formed by the union of C5 and C6 roots. This trunk gives rise to branches such as the suprascapular nerve and the nerve to subclavius. Quiz 2: Which nerve is responsible for innervating the muscles involved in elbow flexion? Radial nerve ✔️ Musculocutaneous nerve Ulnar nerve Axillary nerve Explanation: The musculocutaneous nerve, which arises from the lateral cord of the brachial plexus, innervates muscles like the biceps brachii and brachialis, both of which are responsible for elbow flexion. Quiz 3: Which muscle is affected by injury to the long thoracic nerve? ✔️ Serratus anterior Subscapularis Supraspinatus Biceps brachii Explanation: The long thoracic nerve, arising from C5, C6, and C7, innervates the serratus anterior muscle. Injury to this nerve leads to medial winging of the scapula, causing difficulty in arm elevation. Quiz 4: Which nerve does the medial cord give rise to? ✔️ Ulnar nerve Radial nerve Axillary nerve Musculocutaneous nerve Explanation: The medial cord gives rise to the ulnar nerve, which innervates most of the intrinsic hand muscles and provides sensation to the medial side of the hand.