How A PEM Electrolyser Works (Lesson 2/5) Hunor Kacso | Hydrogen Training Solutions скачать в хорошем качестве
Скачать видео с ютуб по ссылке или смотреть без блокировок на сайте: How A PEM Electrolyser Works (Lesson 2/5) Hunor Kacso | Hydrogen Training Solutions в качестве 4k
У нас вы можете посмотреть бесплатно How A PEM Electrolyser Works (Lesson 2/5) Hunor Kacso | Hydrogen Training Solutions или скачать в максимальном доступном качестве, видео которое было загружено на ютуб. Для загрузки выберите вариант из формы ниже:
-
Информация по загрузке:
Скачать mp3 с ютуба отдельным файлом. Бесплатный рингтон How A PEM Electrolyser Works (Lesson 2/5) Hunor Kacso | Hydrogen Training Solutions в формате MP3:
Если кнопки скачивания не
загрузились
НАЖМИТЕ ЗДЕСЬ или обновите страницу
Если возникают проблемы со скачиванием видео, пожалуйста напишите в поддержку по адресу внизу
страницы.
Спасибо за использование сервиса ClipSaver.ru
How A PEM Electrolyser Works (Lesson 2/5) Hunor Kacso | Hydrogen Training Solutions
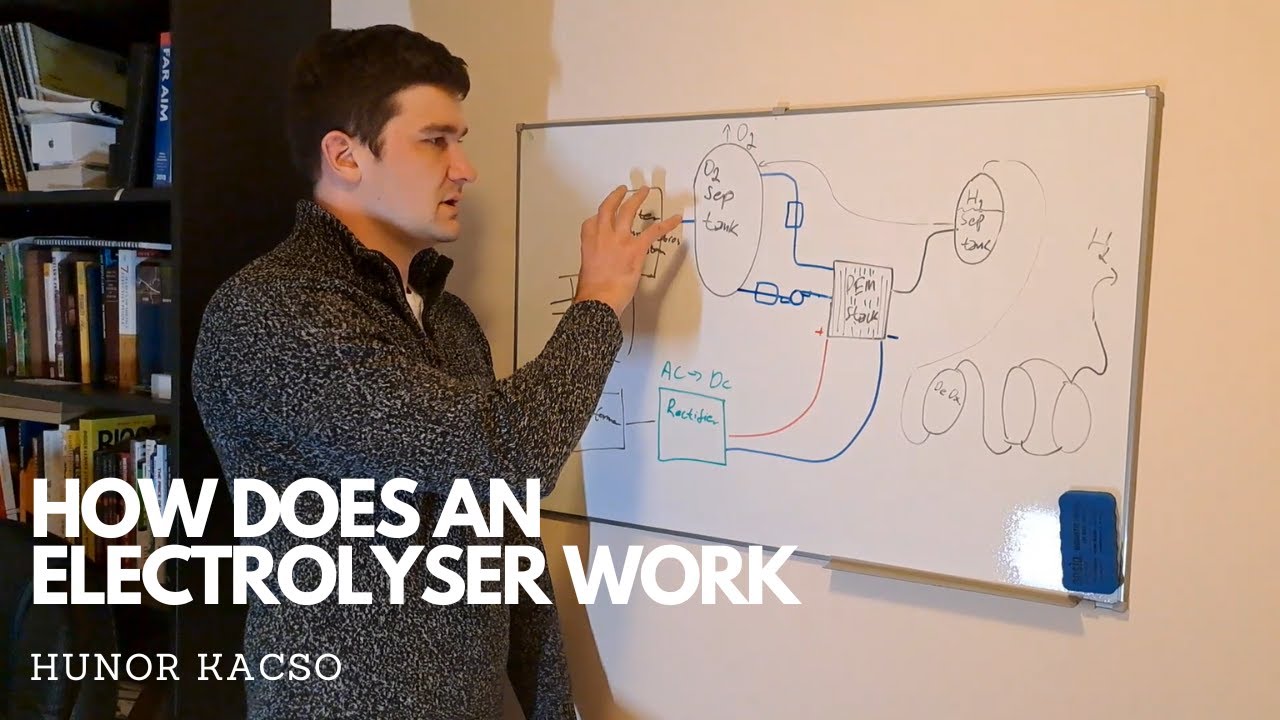
For more content, please join my MASTERCLASS here: https://www.hydrogentrainingsolutions... Video explains the Balance of Plant Operation of a typical PEM Electrolyser system. Polymer electrolyte membrane (PEM) electrolysis is the electrolysis of water in a cell equipped with a solid polymer electrolyte (SPE) that is responsible for the conduction of protons, separation of product gases, and electrical insulation of the electrodes. The PEM electrolyser was introduced to overcome the issues of partial load, low current density, and low pressure operation currently plaguing the alkaline electrolyser. It involves a proton-exchange membrane. One of the largest advantages to PEM electrolysis is its ability to operate at high current densities. This can result in reduced operational costs, especially for systems coupled with very dynamic energy sources such as wind and solar, where sudden spikes in energy input would otherwise result in uncaptured energy. The polymer electrolyte allows the PEM electrolyser to operate with a very thin membrane while still allowing high pressures, resulting in low ohmic losses, primarily caused by the conduction of protons across the membrane and a compressed hydrogen output.









