Quantitative EEG: ADR (Alpha Delta Ratio) скачать в хорошем качестве
Повторяем попытку...
Скачать видео с ютуб по ссылке или смотреть без блокировок на сайте: Quantitative EEG: ADR (Alpha Delta Ratio) в качестве 4k
У нас вы можете посмотреть бесплатно Quantitative EEG: ADR (Alpha Delta Ratio) или скачать в максимальном доступном качестве, видео которое было загружено на ютуб. Для загрузки выберите вариант из формы ниже:
-
Информация по загрузке:
Скачать mp3 с ютуба отдельным файлом. Бесплатный рингтон Quantitative EEG: ADR (Alpha Delta Ratio) в формате MP3:
Если кнопки скачивания не
загрузились
НАЖМИТЕ ЗДЕСЬ или обновите страницу
Если возникают проблемы со скачиванием видео, пожалуйста напишите в поддержку по адресу внизу
страницы.
Спасибо за использование сервиса ClipSaver.ru
Quantitative EEG: ADR (Alpha Delta Ratio)
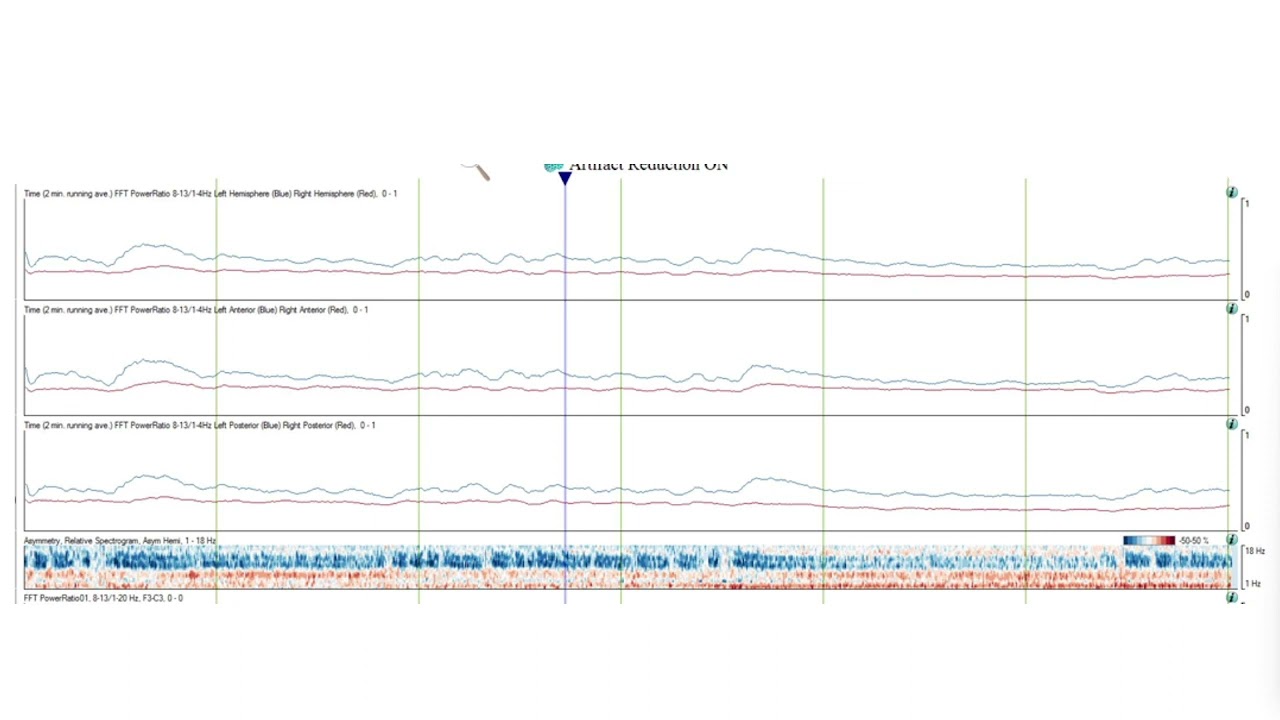
In this short video, we will be discussing Color Density Spectrograms, Alpha Delta Ratio – a trend typically used for detection of ischemia. Alpha-Delta ratio or ADR, as the name suggests, is a ratio of power in the alpha frequency band to the power in delta frequency band. The ratio is typically displayed on a line graph as a moving average of 2-minute long time segments. Just like relative alpha variability, separate location-based trends can be made for each hemisphere, quadrant or six subdivisions including the right and left frontal, centrotemporal and parietooccipital regions. Red line graph typically represent activity on the right side and blue line graph represent activity on the left side. The trend has been most studied for its utility in monitoring for diffuse cerebral ischemia (DCI) in the setting of subarachnoid hemorrhage. As the ischemia develops, there is a relative drop in the alpha frequencies and relative increase in delta activity. This leads to a drop in ADR. In order to minimize the effect of state, post-stimulation ADRs are obtained by periodically stimulating the patients. Claassen et al (2004) reported a cut-off of decrease in ADR by more than 10% below the baseline in at least 6 consecutive recordings (100% sensitivity, 76% specificity) or a single recording with more than 50 % drop in ADR (89% sensitivity, 84% specificity) to be statistically significant for their association with diffuse cerebral ischemia. Rosenthal et al. (2018) used similar cutoff values and also found a statistically significant association of decreasing ADRs with DCI (32.7% vs. 9.8%, OR less than 0.001). Rosenthal et al (2018) utilized a more easily applicable simple visual analysis (eyeballing) of the ADR graphs instead of relying on real-time mathematical calculations. When used in conjunction with other EEG alarms including new epileptiform discharges, new focal slowing and relative alpha variability (RAV); the study predicted DCI in lower risk patients with 91% sensitivity, 83% specificity and higher risk patients with 95% sensitivity and 83% specificity. The DCI was predicted with a median latency of 1.9 days and exceeded by 12 hours in 82% of the cases.



















