Скачать с ютуб Photoelectric effect || stopping potential в хорошем качестве
Скачать бесплатно и смотреть ютуб-видео без блокировок Photoelectric effect || stopping potential в качестве 4к (2к / 1080p)
У нас вы можете посмотреть бесплатно Photoelectric effect || stopping potential или скачать в максимальном доступном качестве, которое было загружено на ютуб. Для скачивания выберите вариант из формы ниже:
Загрузить музыку / рингтон Photoelectric effect || stopping potential в формате MP3:
Если кнопки скачивания не
загрузились
НАЖМИТЕ ЗДЕСЬ или обновите страницу
Если возникают проблемы со скачиванием, пожалуйста напишите в поддержку по адресу внизу
страницы.
Спасибо за использование сервиса ClipSaver.ru
Photoelectric effect || stopping potential
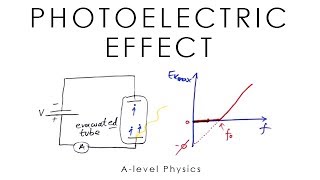
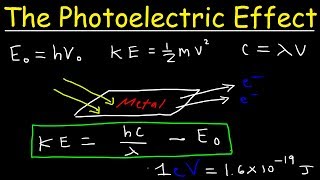
Q.What is photoelectric effect? Ans:The phenomenon of ejection of electrons from the surface of a metal when light of suitable frequency strikes on it, is called photoelectric effect. The emitted electrons are called photoelectrons.” Experimental studies of photoelectric effect under different conditions led to the following important observations— (i) The electrons are ejected from the metal surface as soon as the beam of light strikes the surface. . (ii) For each metal, certain minimum frequency of light is needed to eject the electrons. This is known as threshold frequency and it is different for different metals. (iii) The kinetic energy of the ejected electrons is directly proportional to the frequency of the incident radiation and it is independent of its intensity. (iv) The number of electrons ejected per second from the metal surface depends upon the intensity or brightness of incident radiation but does not depend upon its frequency work function & Threshold frequency For a given metal surface, there exists a certain minimum frequency of incident radiation below which no photoelectrons are emitted. This frequency is called the threshold frequency. Increasing the frequency of the incident beam, keeping the number of incident photons fixed (this would result in a proportionate increase in energy) increases the maximum kinetic energy of the photoelectrons emitted. Thus the stopping voltage increases (see the experimental setup in the figure). The number of electrons also changes because of the probabilitythat each photon results in an emitted electron are a function of photon energy. If the intensity of the incident radiation of a given frequency is increased, there is no effect on the kinetic energy of each photoelectron. stopping potential If we apply a negative potential to the collector plate Q with respect to the plate P and gradually increase it, the photoelectric current decreases, becoming zero at a certain negative potential. The negative potential on the collector at which the photoelectric current becomes zero is called the stopping potential or cut off potential. i. For a given frequency of incident radiation, the stopping potential is independent of its intensity. ii. For a given frequency of incident radiation, the stopping potential is determined by the maximum kinetic energy of the photoelectrons that are emitted. If qe is the charge on the electron and V is the stopping potential, then the work done by the retarding potential in stopping the electron