Скачать с ютуб Left Ventricular Pressure Volume Loop в хорошем качестве
Скачать бесплатно и смотреть ютуб-видео без блокировок Left Ventricular Pressure Volume Loop в качестве 4к (2к / 1080p)
У нас вы можете посмотреть бесплатно Left Ventricular Pressure Volume Loop или скачать в максимальном доступном качестве, которое было загружено на ютуб. Для скачивания выберите вариант из формы ниже:
Загрузить музыку / рингтон Left Ventricular Pressure Volume Loop в формате MP3:
Если кнопки скачивания не
загрузились
НАЖМИТЕ ЗДЕСЬ или обновите страницу
Если возникают проблемы со скачиванием, пожалуйста напишите в поддержку по адресу внизу
страницы.
Спасибо за использование сервиса savevideohd.ru
Left Ventricular Pressure Volume Loop
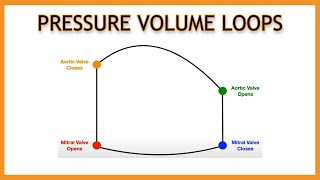
The volume-pressure loop of the heart, also known as the left ventricular pressure-volume loop, is a graphical representation of the relationship between the pressure and volume in the left ventricle during one cardiac cycle. It is divided into several distinct phases that illustrate the mechanical function of the heart. The first phase, isovolumetric contraction, begins with the closure of the mitral valve and ends with the opening of the aortic valve. During this phase, the volume within the left ventricle remains constant as the ventricle contracts, leading to a rapid increase in pressure. This phase is represented by a vertical line moving upwards on the right side of the loop. Key events in this phase include the closure of the mitral valve and the maintenance of a closed aortic valve, resulting in a rapid rise in ventricular pressure. Following isovolumetric contraction is the ventricular ejection phase. This phase starts with the opening of the aortic valve and ends with its closure. The volume of the ventricle decreases as blood is ejected into the aorta, with the pressure initially rising to a peak before beginning to decrease. This phase forms the top curved part of the loop, moving from right to left. Key events during this phase include the opening of the aortic valve, the ejection of blood from the ventricle, the attainment of peak systolic pressure, and the subsequent closure of the aortic valve. The next phase, isovolumetric relaxation, begins with the closure of the aortic valve and ends with the opening of the mitral valve. During this phase, the volume of the ventricle remains constant as it relaxes, causing the pressure to drop sharply. This phase is represented by a vertical line moving downwards on the left side of the loop. Important events in this phase include the closure of the aortic valve and a rapid decrease in ventricular pressure while the mitral valve remains closed. The final phase of the loop is ventricular filling. This phase begins with the opening of the mitral valve and ends with its closure. During ventricular filling, the volume of the ventricle increases as blood flows in from the left atrium, while the pressure remains relatively low and constant. This phase forms the bottom curved part of the loop, moving from left to the right. Key events in this phase include the opening of the mitral valve, passive filling of the ventricle (initially rapid then slower), atrial contraction, and the eventual closure of the mitral valve. Stroke volume (SV) and stroke work (SW) are key parameters derived from the pressure-volume loop that provide insights into the mechanical performance of the heart. Stroke Volume (SV) Stroke volume is the amount of blood ejected by the left ventricle during each cardiac cycle. It is calculated as the difference between the end-diastolic volume (EDV) and the end-systolic volume (ESV): 𝑆𝑉=𝐸𝐷𝑉−𝐸𝑆𝑉 In the pressure-volume loop, stroke volume is represented by the horizontal distance between the points corresponding to the end of diastole and the end of systole on the volume axis. A larger stroke volume indicates a greater amount of blood being pumped out of the ventricle with each heartbeat, which is crucial for maintaining adequate cardiac output and tissue perfusion. Stroke Work (SW) Stroke work is the amount of work performed by the heart to eject blood during each cardiac cycle. It is represented by the area enclosed within the pressure-volume loop. Stroke work can be calculated by integrating the ventricular pressure over the change in volume during systole. This area represents the mechanical energy generated by the ventricle to overcome both the resistive and elastic components of the arterial system. Stroke work is an important indicator of the heart's efficiency and energy expenditure. Higher stroke work signifies a more energetically demanding cardiac cycle, which can be seen in conditions with increased afterload, such as hypertension.