Lower Limb Anatomy, Human Anatomy, USMLE Step 1 - Full Vignette with Extended Explanations скачать в хорошем качестве
Повторяем попытку...
Скачать видео с ютуб по ссылке или смотреть без блокировок на сайте: Lower Limb Anatomy, Human Anatomy, USMLE Step 1 - Full Vignette with Extended Explanations в качестве 4k
У нас вы можете посмотреть бесплатно Lower Limb Anatomy, Human Anatomy, USMLE Step 1 - Full Vignette with Extended Explanations или скачать в максимальном доступном качестве, видео которое было загружено на ютуб. Для загрузки выберите вариант из формы ниже:
-
Информация по загрузке:
Скачать mp3 с ютуба отдельным файлом. Бесплатный рингтон Lower Limb Anatomy, Human Anatomy, USMLE Step 1 - Full Vignette with Extended Explanations в формате MP3:
Если кнопки скачивания не
загрузились
НАЖМИТЕ ЗДЕСЬ или обновите страницу
Если возникают проблемы со скачиванием видео, пожалуйста напишите в поддержку по адресу внизу
страницы.
Спасибо за использование сервиса ClipSaver.ru
Lower Limb Anatomy, Human Anatomy, USMLE Step 1 - Full Vignette with Extended Explanations
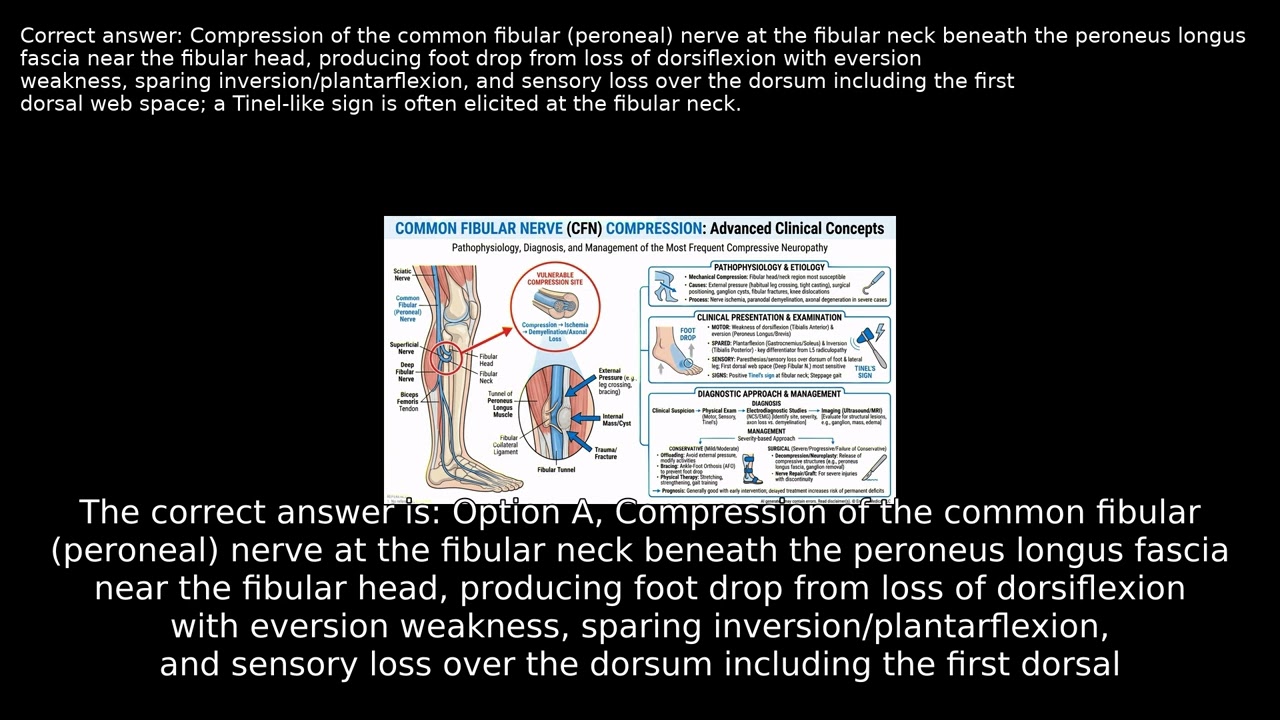
A 46-year-old woman develops a right steppage gait with foot slapping and sensory loss on the dorsum of her foot after prolonged periods of sitting, leg crossing, and kneeling at work. With normal spine and knee imaging but notable leg weakness and numbness, what clinical features and provocative findings help identify the specific anatomic site responsible for her symptoms? VIDEO INFO Category: Lower Limb Anatomy, Human Anatomy, USMLE Step 1 Difficulty: Hard - Advanced level - Challenges experienced practitioners Question Type: Diagnostic Failure Case Type: Resource Limited Explore more ways to learn on this and other topics by going to https://endlessmedical.academy/auth?h... QUESTION A 46-year-old woman presents to a remote critical access clinic 8 hours after discharge from a regional ED for observation following a worksite heat exposure. She reports a 3-week history of repeatedly tripping on uneven ground and a sensation that her right foot slaps when she walks long distances at the plant. She denies back pain, radiating leg pain, saddle anesthesia, bowel or bladder dysfunction, or weight loss beyond 7 lb during a recent diet challenge.... OPTIONS A. Compression of the common fibular (peroneal) nerve at the fibular neck beneath the peroneus longus fascia near the fibular head, producing foot drop from loss of dorsiflexion with eversion weakness, sparing inversion/plantarflexion, and sensory loss over the dorsum including the first dorsal web ... B. Entrapment of the superficial fibular (peroneal) nerve at its fascial exit in the distal lateral leg, typically causing dorsal foot paresthesias that spare the first web space with eversion weakness only; isolated distal entrapment does not produce global foot drop or a Tinel sign at the fibular ... C. Entrapment of the deep fibular (peroneal) nerve in the anterior tarsal tunnel beneath the inferior extensor retinaculum, which classically causes first dorsal web-space numbness and extensor hallucis brevis weakness; ankle-level disease would not explain eversion weakness or a positive Tinel sign... D. L5 radiculopathy affecting the traversing L5 root, expected to produce dorsiflexion weakness with frequent inversion and hip abduction deficits, often with low back pain and positive straight-leg raise; this pattern is unlikely with a normal lumbar MRI and preserved inversion and proximal strength. CORRECT ANSWER A. Compression of the common fibular (peroneal) nerve at the fibular neck beneath the peroneus longus fascia near the fibular head, producing foot drop from loss of dorsiflexion with eversion weakness, sparing inversion/plantarflexion, and sensory loss over the dorsum including the first dorsal web space; a Tinel-like sign is often elicited at the fibular neck. EXPLANATION The patient s pattern of weakness and sensory loss localizes best to a lesion at the fibular neck where the common fibular (peroneal) nerve is especially superficial and vulnerable to external compression. Dorsiflexion 2/5 on the Medical Research Council scale (active movement with gravity eliminated) with eversion weaker than inversion, preserved plantarflexion, sensory loss over the dorsum of the foot most marked in the first dorsal web space, and a Tinel-like sign at the fibular neck are the classic bedside constellation.... --------------------------------------------------- Our cases and questions come from the https://EndlessMedical.Academy quiz engine - multi-model platform. Each question and explanation is forged by consensus between multiple top AI models (GPT, Claude, Grok, etc.), with automated web searches for the latest research and verified references. Calculations (e.g. eGFR, dosages) are checked via code execution to eliminate errors, and all references are reviewed by several AIs to minimize hallucinations. Important note: This material is entirely AI-generated and has not been verified by human experts; despite stringent consensus checks, perfect accuracy cannot be guaranteed. Exercise caution - always corroborate the content with trusted references or qualified professionals, and never apply information from this book to patient care or clinical decisions without independent verification. Clinicians already rely on AI and online tools - myself included - so treat this book as an additional focused aid, not a replacement for proper medical education. Visit https://endlessmedical.academy for more AI-supported resources and cases. This material can not be treated as medical advice. May contain errors. ---------------------------------------------------












![Анатомическое положение и направления [Анатомия УПРОЩЕНА]](https://image.4k-video.ru/id-video/t6-ueqFK1IE)






